From Vision to Venture: Mastering Business Setup in India

India is witnessing a dynamic entrepreneurial revolution, fueled by innovation, digital transformation, and a supportive policy framework. From tech-savvy startups to traditional businesses remained, the journey from a mere business idea to a registered, operational entity is more achievable than ever. However, success in business setup in India demands more than just passion—it requires a clear roadmap, legal compliance, and strategic decision-making.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide for aspiring entrepreneurs looking to transform their vision into a thriving venture in India. Whether you are planning a small-scale enterprise or aiming to launch a scalable startup, understanding the fundamentals of business setup in India is your first step toward sustainable growth and long-term.
Choosing the Right Business Structure
Selecting an appropriate structure is a critical step in the business setup in India journey. Your chosen structure directly influences the process of company registration in Indiaincluding compliance requirements and tax implications. Therefore, understanding each option is essential to make an informed decision aligned with your vision and scale of operations.
Here’s a breakdown of the major structures needed to start a business in India:| Particulars | Ideal for | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorship | Individuals running a small business or freelancing | Easiest to set up and operate with minimal compliance | Full control, simple registration, low cost | Unlimited personal liability, limited funding options, not a separate legal entity |
| Partnership Firm | Two or more individuals working together with shared responsibility | Governed by the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 | Easy to start, shared capital and responsibilities | Partners have unlimited liability, lesser credibility with investors |
| Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) | Professionals and small businesses looking for liability protection | Combines benefits of a partnership with limited liability of a company | Separate legal entity, limited liability, low compliance compared to companies | Cannot issue shares, limited scalability for large ventures |
| Private Limited Company | Startups, businesses seeking scalability and investment | Regulated under the Companies Act, 2013. Can raise equity funding | Separate legal identity, limited liability, easier access to investors | Higher compliance, annual filings, statutory audits mandatory |
| One Person Company (OPC) | Solo entrepreneurs who want the benefits of a company structure | Introduced under the Companies Act, 2013 | Limited liability, separate legal identity, full control with a single founder | Limited to one shareholder, restricted fundraising options |
| Section 8 Company (Non-Profit) | Charitable, social, or not-for-profit organizations | Must apply its profits toward the promotion of its objectives | Tax exemptions, credibility for grants and donations | Strict regulatory oversight, cannot distribute profits |
| Public Limited | Large businesses planning to raise capital from the public. | Can raise capital by offering shares to the public and is governed by strict regulatory compliance | Can raise large capital from the public through share issuance. | Subject to strict regulatory compliance and disclosure norms. |
Know More About: Trademark Registration Services in Delhi India
Steps to Register Your Business in IndiaTo start a business in India you need to follow the following steps:
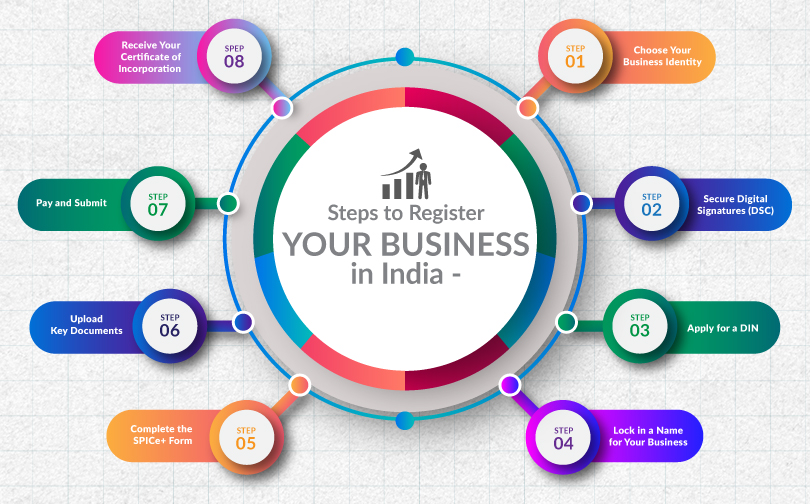
| Choose Your Business Identity | The business setup in India process involves multiple legal and documentation steps, which begin with choosing your entity type. Decide what form your business will take. Your decision will shape how you are taxed, how you raise funds, and how much personal liability you take on. |
| Secure Digital Signatures (DSC) | Get a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for all directors or partners; it’s needed to sign online forms on the MCA portal. |
| Apply for a DIN (Director Identification Number) | If you are planning to be a company director, you will need a Director Identification Number. |
| Lock in a Name for Your Business | Choose a name that reflects your vision and meets legal guidelines. Submit it for approval through RUN (Reserve Unique Name) or directly in SPICe+ Part A. |
| Complete the SPICe+ Form (Part B) | SPICe+ is your all-in-one application. Here, you can: Register your business, Get your DIN, Apply for PAN, TAN, GST, EPFO, ESIC |
| Upload Key Documents | 1. Identity and address proof of founders 2. Proof of business address 3. MOA & AOA (the company’s blueprint) 4. Declarations and consent forms |
| Pay and Submit | Submit your SPICe+ form on the MCA portal with the prescribed fee |
| Receive Your Certificate of Incorporation (COI) | Once approved, your company officially comes to life. You will receive a Certificate of Incorporation (COI) with a Corporate Identification Number (CIN) — your company’s unique legal ID |
Licenses and Compliance Requirements
Once company registration in India is complete, businesses must secure specific licenses based on their industry and stay on top of compliance requirements. The compliance is non-negotiable in the context of business setup in India.
Here’s what you need to consider:- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Registration: If your annual turnover exceeds the prescribed threshold (Rs 20–Rs 40 lakh depending on your state and business type), GST registration is mandatory.
- Shops and Establishment License: If you have a physical office, shop, or commercial workspace, this license is often compulsory under your respective state’ labor department.
- Import-Export Code (IEC): Planning to trade globally? You will need an >Import Export Code (IEC)issued by the Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT). This is essential for customs clearance, bank remittances, and international invoicing.
- MSME/Udyam Registration: While not mandatory, registering as an MSME (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprise) via Udyam can unlock government incentives, easier bank loans, subsidies, and protection against delayed payments.
- EPFO and ESIC Registrations: If your business employs more than 10 (ESIC) or 20 (EPFO) employees, you must register under Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) and Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC).
Opening a Business Bank Account
Once your business is legally registered, the next critical step is to open a dedicated business bank account. This isn’t just a formality; it’s a legal requirement for most registered entities and a smart move for any serious entrepreneur. It separates your personal finances from your business, builds credibility, and prepares you for growth, investment, and compliance. Banks require incorporation certificates issued after company registration in India for opening a current account.
Funding Your StartupYou have got the idea. You have got the structure. Now you need the capital. If you are planning to start a business in India, understanding your funding options is critical to long-term sustainability. Funding is the fuel that powers your startup journey, from minimum viable product to market and from prototype to profitability. Whether you are bootstrapping or dreaming of venture capital, India offers a growing ecosystem of funding opportunities for startups at every stage.
Taxation and Accounting EssentialsRunning a business isn’t just about earning revenue; it is also about managing it wisely and staying compliant with India’s tax and accounting regulations. Whether you are a solopreneur or a funded startup, a sound understanding of your tax obligations and financial reporting is essential to avoid penalties and to build long-term credibility. Keeping your tax and accounting game tight isn’t just about compliance—it’s about professionalism, trust, and future readiness.
Building a Winning Team
Behind every great business is a great team. Your idea may set the vision, but your team brings it to life. In India’s competitive startup and business landscape, building the right team isn’t just about filling roles; it’s about hiring people who align with your mission, culture, and growth plan. A strong team aligned with a clear mission is the most valuable asset your business can have—it drives innovation, fuels growth, and ensures long-term sustainability.
Marketing and Going DigitalIn today’s hyper-connected world, it is not enough to build a great product or service; you need people to know about it, trust it, and talk about it. That’s where smart marketing and digital presence come into play. For Indian startups and businesses, going digital is not just optional; it is essential for visibility, credibility, and growth.
Challenges to Anticipate and How to Overcome Them
Starting a business in India can be as rewarding as it is demanding. While the entrepreneurial landscape is rich with opportunity, it comes with its fair share of hurdles. Awareness of these challenges and how to tackle them head-on can make the difference between survival and success.
- Regulatory Hurdles and Red Tape: Despite digital reforms, navigating India's bureaucratic system can still be time-consuming, especially for permits, tax registrations, and industry-specific licenses. You can engage with a certified company secretary (CS) or chartered accountant (CA) for compliance support. Use platforms like the Startup India portal and MCA21 to fast-track registrations.
- Access to Funding: Raising capital is often a bottleneck, particularly for first-time founders with no collateral or prior entrepreneurial track record. Start with bootstrapping or small-ticket loans. Leverage pitch events, incubators, and government schemes. Build a strong pitch deck and MVP to attract angel investors or early-stage VCs.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: Startups often struggle to attract skilled professionals due to limited resources and brand recognition. You can offer equity-based incentives. Create a culture of learning, ownership, and flexibility.
- Market Competition and Customer Acquisition: With increasing saturation in many sectors, breaking through the noise and acquiring customers is tough. Identify a unique value proposition (UVP) and target niche markets first. Focus on content marketing, SEO, and influencer collaborations for organic reach.
- Managing Cash Flow and Financial Discipline: Improper budgeting or delayed payments can cripple operations, especially in the early days. Maintain real-time financial tracking using tools. Establish clear payment terms with clients and vendors. Keep a 3–6 month runway for emergencies.
- Digital & Cybersecurity Risks: In the race to digitize, startups often overlook data protection and cybersecurity. Invest in basic cybersecurity infrastructure—firewalls, SSL, and anti-virus. Ensure compliance with India’s data protection laws.
Turning your business idea into a thriving venture in India requires more than just ambition—it demands planning, adaptability, and execution. From choosing the right structure and navigating registrations to securing funding and building a team, each step is a milestone in your entrepreneurial journey. Embracing digital tools, staying compliant, and leveraging government initiatives can give you a competitive edge. While challenges are inevitable, strategic foresight and resilience can turn obstacles into opportunities. With careful planning and execution, business setup in India can transform your vision into a lasting venture.
Read Also:Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) –
Q.1 What is the first step for business setup in India?
The first step for business setup in India is choosing the right business structure.
Q.2 How do I register a company in India?To register a company in India you must obtain Digital Signatures (DSC), apply for a Director Identification Number (DIN), reserve your business name through RUN or SPICe+, complete the SPICe+ form, and submit required documents on the MCA portal.
Q.3 Is GST registration mandatory for all businesses in India?No, GST registration is only mandatory if your annual turnover exceeds the specified threshold (Rs 20–40 lakhs depending on the state and business type).
Q.4 Do I need a business bank account for my startup in India?Yes, once your business is registered, a separate business bank account is legally required.
Q.5 What are the common challenges in starting a business in India?Common challenges include regulatory red tape, limited funding access, talent acquisition, intense market competition, cash flow management, and cybersecurity risks.

