How Foreign Companies Can Establish a Branch Office in India

Introduction – Why Set Up a Branch Office in India
Setting up a branch office in India is an appealing strategic choice for foreign companies looking to expand their business footprint in one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing markets. A branch office acts as an extension of the parent company, allowing it to conduct business activities within India while maintaining control from the head office. India offers vast market potential due to its large consumer base, growing middle class, and favorable economic environment.
Establishing a branch office in India is simpler and more cost-effective compared to setting up a fully independent subsidiary, making it an ideal option for companies testing the market or seeking to serve regional customers, provide technical support, or carry out consultancy and trading activities. Moreover, a branch office helps companies build local brand presence, improve communication with customers, and gain insights into the Indian market and regulatory landscape.
A foreign company branch office India enables businesses to capitalize on local opportunities without the long-term commitment of forming a separate legal entity. However, foreign companies need to secure RBI approval for branch office in India and comply with various legal and regulatory requirements to ensure transparent and compliant operations. Overall, a branch office in India offers a flexible, efficient, and effective gateway for international firms to tap this dynamic market’s growth potential and enhance their regional reach.
What Is a Branch OfficeA branch office is a secondary location of a company that operates separately from the main office but is not a separate legal entity. It functions as an extension of the parent company, conducting the same or substantially similar business activities. Unlike a subsidiary, a branch office’s liabilities and legal responsibilities lie with the parent company. Typically, a branch office has a branch manager who reports directly to the head office's management.
Companies that establish a branch office in India can expand their geographical presence, allowing them to perform operations such as sales, marketing, trading, and services across the country. They facilitate market penetration, customer interaction, and local operations without creating a separately incorporated entity. This structure helps companies maintain control over their operations while expanding their reach efficiently. However, the parent company assumes full responsibility for the branch office’s activities and any related legal or financial obligations.
Key Features of a Branch Office in India
- Foreign company branch office India is an extension of the foreign parent company and not a separate legal entity.
- The branch office can undertake activities such as import/export, consultancy, research, and promotion of technical or financial collaboration but cannot engage in manufacturing activities.
- All profits earned by the branch office are repatriated to the parent company abroad.
- The branch in India must comply with Indian regulations, including registration with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) and adherence to the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) rules.
- RBI approval for branch office in India is mandatory before setting up operations, ensuring the company meets all eligibility and compliance conditions.
- The branch office must maintain proper books of accounts, file annual financial statements, and appoint an authorized representative to liaise with Indian regulatory authorities.
- It must obtain tax registrations, including Permanent Account Number (PAN), Tax Deduction Account Number (TAN), and Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration if it conducts taxable business operations.
- The branch office’s liabilities and obligations directly rest with the foreign parent company.
- Registration with the ROC requires submission of Form FC-1 and related documents within 30 days of RBI approval.
- Documents for RBI approval include board resolution, incorporation certificate, audited financial statements, and KYC details of the authorized signatory.
- Additional compliance includes adherence to Indian tax laws and filing of tax returns as per Indian regulations.
- The foreign company must be a body corporate incorporated outside India.
- The company should have a consistent profitable track record in the immediately preceding five financial years in its home country.
- The net worth of the company should be at least USD 100,000 or its equivalent.
- The foreign company branch office India must have the same name as the parent foreign company.
- The foreign company should obtain RBI approval for branch office in India under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
- The foreign company must submit the application in Form FNC-1 through an Authorized Dealer Category-I bank for RBI approval.
- After obtaining RBI approval, the branch office must be registered with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) within 30 days by filing Form FC-1 along with required documents.
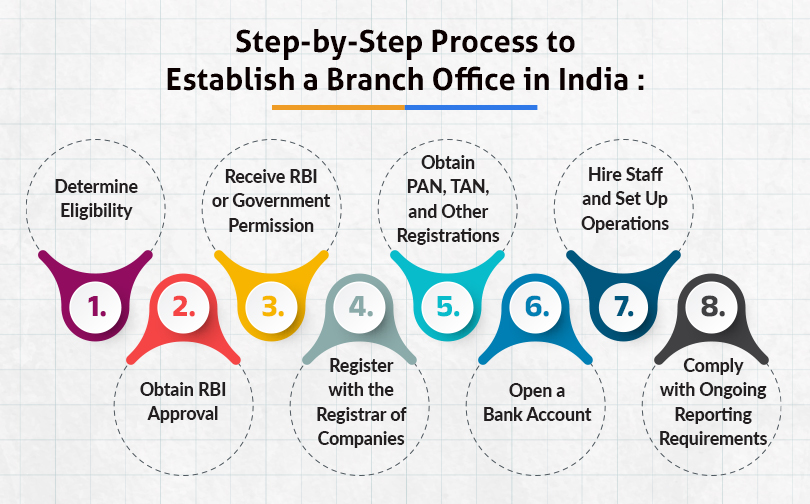
To establish a branch office in India, a foreign company must go through RBI approval, company registration, and compliance with Indian tax laws. The following process is followed:
- Determine Eligibility: The foreign company must be financially sound and have a profitable track record. Generally, it should have a net worth of at least USD 100,000 and a history of profitability in its home country for the last five years.
- Obtain RBI Approval: Foreign companies must apply to the RBI through an Authorized Dealer (AD) Category-I Bank to get approval for establishing a branch office. The application is made using Form FNC, along with supporting documents like the company’s financial statements and incorporation certificate.
- Receive RBI or Government Permission: Depending on the nature of the business, approval may come directly from the RBI or the Government of India through the Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB), especially for sectors requiring government clearance.
- Register with the Registrar of Companies (ROC): Once RBI approval is granted, the company must register the branch office with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) by filing Form FC-1 within 30 days of establishing the office in India.
- Obtain PAN, TAN, and Other Registrations: The branch office in India must obtain a Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) from the Income Tax Department. Depending on its business activities, it may also need to register for GST, Professional Tax, and Import Export Code (IEC).
- Open a Bank Account: The company must open a bank account in India in the name of the branch office to manage its financial transactions.
- Hire Staff and Set Up Operations: Once registered, the foreign company branch office India can hire local staff, enter into contracts, and begin operations within the scope of activities permitted by the RBI.
- Comply with Ongoing Reporting Requirements: After establishment, the branch office must regularly submit audited financial statements, annual activity certificates, and other required filings to the RBI, ROC, and Income Tax Department.
Documents Required for Approval
To establish a branch office in India, the following documents are typically required for RBI approval and registration.
- Application letter to RBI through an Authorized Dealer (AD) Category-I bank.
- Board resolution of the parent company approving the establishment of a branch office in India.
- Certified copies of the Certificate of Incorporation or Registration of the parent company.
- Memorandum and Articles of Association of the parent company.
- Latest audited financial statements of the parent company (for the last five years or as applicable).
- Details of the parent company’s directors and shareholders.
- Address proof and details of the proposed branch office in India.
- Project report or details explaining the business activities to be undertaken in India.
- No-objection certificate from the parent company for opening the branch office.
- Letter of comfort from the parent company (if applicable) guaranteeing support to the branch.
- Undertaking stating no legal proceedings against the company in India and compliance with Indian laws.
- Auditor’s certificate regarding liabilities and repatriation of funds (if applicable).
- RBI approval or clearance from sectoral regulators (if the business activity is regulated).
- Any other documents as requested specifically by RBI depending on the sector or location of the branch.
- Submission of application for RBI approval through an Authorized Dealer bank begins the process. RBI normally takes around 4 to 8 weeks to approve the application.
- After receiving RBI approval, the foreign company must register the branch office with the Registrar of Companies within 30 days by filling out Form FC-1.
- The branch office in India must be opened and operational within 6 months from the date of RBI approval. If not opened within this period, the approval stands cancelled unless an extension is granted by the RBI through the Authorized Dealer bank.
- An extension for opening the branch office can be requested for an additional 6 months. Any further extension beyond these 12 months requires fresh RBI approval.
Permitted activities for a branch office in India:
- Providing professional or consultancy services.
- Conducting research work in areas where the parent company is engaged.
- Promoting technical or financial collaboration between Indian companies and the parent or overseas group company.
- Acting as a buying or selling agent in India or representing the parent company.
- Providing services related to information technology and software development.
- Rendering technical support for products supplied by the parent or group companies.
- Representing foreign airline or shipping companies in India.
- Export/import of goods.
Know More About: company registration services
Restricted activities for a branch office in India:
- Branch offices are generally prohibited from engaging in manufacturing or processing activities directly or indirectly, except if operating in designated Special Economic Zones (SEZs) with specific RBI approval.
- Retail trading activities of any nature are not allowed for branch offices.
- Foreign law firms are barred from opening branch offices in India.
- Any activity beyond what is permitted by the RBI under the Foreign Exchange Management Act is restricted.
- Branch offices must operate only in the sectors and activities in which their parent company is engaged.
The following is the post-establishment branch office compliance in India:
Registration with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA):- The foreign company must register the branch office in India with the MCA by filling out Form FC-1 within 30 days of establishment.
- Submit documents such as the RBI approval letter, certified incorporation certificate, power of attorney, and proof of office address.
- Prepare and file audited financial statements annually with the ROC.
- File annual return and other necessary documents under the Companies Act.
- Submit financial statements of the branch office as part of the parent company’s consolidated accounts.
- Report all foreign exchange transactions related to the branch office to the RBI.
- File periodic Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) returns.
- Obtain PAN and TAN.
- Register for Goods and Services Tax (GST) if applicable.
- File income tax returns and comply with Indian tax laws.
- Submit annual activity reports to the RBI through the Authorized Dealer bank detailing operations and repatriation of funds.
- Maintain records of all RBI approvals and correspondence.
- Comply with applicable labour laws, professional taxes, municipal licenses, and any sector-specific regulatory requirements.
- Maintain proper books in India as per Indian accounting standards.
- Ensure audit and compliance with Indian financial reporting requirements.
Taxation Rules for Branch Offices in India
- A branch office is considered a Permanent Establishment (PE) of the foreign company in India. Hence, it is taxed on income earned or accrued in India as per Indian tax laws.
- The branch office is taxed at the rate applicable to foreign companies, which is 35% plus applicable surcharge and cess.
- Transactions between the branch office and its parent company are subject to transfer pricing regulations. These rules require transactions to be at arm’s length to ensure appropriate allocation of profits and taxation.
- The branch office must maintain separate books of accounts for its Indian operations, get them audited, and file Indian income tax returns annually.
- There is no withholding tax on remittance of branch office profits to the parent company abroad. However, profits are taxable in India before remittance.
- The branch office is also liable for GGoods and Services Tax (GST) and withholding taxes on contract payments, salaries, and other applicable indirect taxes.
- Branch offices can engage only in activities permitted by the RBI.
- A branch office is not a separate legal entity but an extension of the foreign parent company. This means the parent company is fully liable for the branch office’s activities, debts, and obligations.
- Establishing a branch office requires prior RBI approval and continuous regulatory compliance under the Companies Act and FEMA regulations, imposing procedural complexity.
- A branch office cannot raise capital or equity in India, as it is not an independent legal entity, limiting its growth and financial options.
- Though profits can be repatriated to the parent company without withholding tax, the branch office must pay taxes in India on income earned.
- A branch office’s existence is dependent on the parent company and regulatory approvals. Its existence can be terminated easily upon withdrawal of approval.
- Branch offices must comply with Indian accounting, tax, labour, and other local laws, creating administrative overhead.
Conclusion
Foreign companies can establish a branch office in India as an effective way to expand their presence in the vast and growing market. A branch office acts as an extension of the parent company, allowing operational control while offering localized services such as consultancy, technical support, export-import activities, and research. The process requires prior approval from the RBI, compliance with the Companies Act, and registration with the Registrar of Companies (ROC).
Although a branch office simplifies market entry compared to setting up a subsidiary, it comes with limitations such as restricted business activities, dependency on the parent company for liabilities, and regulatory compliance. Despite these constraints, setting up a branch office remains a strategic, flexible, and cost-effective gateway for foreign firms aiming to tap India's economic potential and enhance regional reach. With adherence to the regulatory framework and ongoing compliance, branch offices enable foreign companies to establish a credible footprint in India’s dynamic market. A branch office in India is an effective and practical way for global companies to expand into the Indian market.
We provide expert assistance in setting up branch offices in India, ensuring smooth RBI approval, ROC registration, and full compliance. Our services include documentation, bank account setup, tax registration, and ongoing regulatory support, making your India entry seamless and hassle-free. Start your business journey with us today!
Read Also:Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) –
Q.1 What is a branch office in India for a foreign company?A branch office is an extension of a foreign company that carries out business operations in India.
Q.2 Who can set up a branch office in India?Only foreign companies with a profitable track record and a net worth of at least USD 100,000 are eligible to establish a branch office in India, subject to RBI approval.
Q.3 What is the process for establishing a branch office in India?The process involves obtaining RBI approval, registering with the Registrar of Companies (ROC), getting PAN and TAN, and completing necessary tax and compliance registrations before starting operations.
Q.4 Is RBI approval mandatory for setting up a branch office?Yes. RBI approval is compulsory for all foreign companies wishing to establish a branch office in India.
Q.5 Can a branch office in India earn income?Yes, a branch office can generate income from permitted activities such as professional services, trading, and consultancy.

