Types of GST Returns: GSTR-1, GSTR-3B & More Explained

Introduction to GST Returns
A GST return is a legal document summarizing a taxpayer’s business activity, and the GST return process ensures that this information is accurately reported to the tax authorities. It includes details of all sales (outward supplies), purchases (inward supplies), tax collected on sales (output tax), and tax paid on purchases (input tax). GST return filing is mandatory for all entities registered under India’s Goods and Services Tax regime, including regular businesses, composition scheme dealers, non-resident taxpayers, and specialized categories, and knowing the correct GST return due dates helps avoid penalties and interest.
Key Features of GST Return- Details Provided: Each return reports sales, purchases, collected and paid GST, and input tax credit for the relevant period.
- Purpose: These filings enable tax authorities to calculate net GST liability, and the GST return process ensures timely compliance and proper credit allocation. Timely GST return filing is crucial for avoiding penalties.
- Who Should File: Anyone registered under GST is required to file returns, and the process is now streamlined through GST filing online, making compliance easier for all categories of taxpayers.
Overview of Different Types of GST Returns:
India’s GST system features several returns tailored to different taxpayer categories, and GST return filing requirements vary depending on registration type. Common returns include GSTR-1 (details of outward supplies/sales), GSTR-3B (monthly/quarterly summary return), GSTR-4 (annual return for composition dealers), and GSTR-9 (annual consolidated return).
Specialized returns are filed by e-commerce operators (GSTR-8), non-resident taxpayers (GSTR-5), TDS deductors (GSTR-7), Input Service Distributors (GSTR-6), and UIN holders (GSTR-11). Each type of GST return has its own format, purpose, and GST return due dates, depending on whether it is filed monthly, quarterly, or annually. Whether monthly, quarterly, or annually, all returns can be submitted through the GST filing online process using the GST portal.
Types of GST Return:
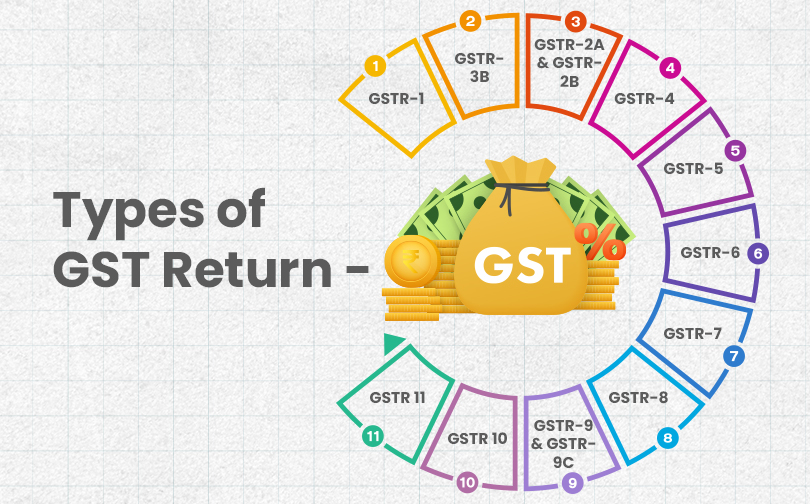
GSTR-1 is a Goods and Services Tax (GST) return filed by normal and casual registered taxpayers in India, summarizing all outward supplies (sales of goods and services) made during a specific tax period, monthly or quarterly, depending on the business turnover.
Key elements of GSTR-1- Invoice-wise details for B2B supplies: Includes both interstate and intrastate sales to registered persons.
- Details of large B2C supplies: Intra-state supplies to unregistered persons and inter-state supplies of value up to Rs 2.5 lakh, reported rate-wise.
- Consolidated B2C supplies: Intra-state supplies to unregistered persons and inter-state supplies of value up to Rs 2.5 lakh, reported rate-wise.
- Credit and Debit Notes: Issued during the period for any amendments to invoices.
- Exports, reverse charge supplies, nil-rated and exempt supplies: Reported separately.
- HSN-wise summary of goods and services supplied.
- Details of advances received or adjusted in the tax period.
Know More About: LLP Registration Services in Delhi India
GSTR-3B: Summary Return for Tax Payment
GSTR-3B is a simplified, monthly summary return under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India. It is used by registered taxpayers to declare a summary of their outward supplies (sales), inward supplies liable to reverse charge, input tax credit (ITC) claimed, and their net tax liability for a given tax period.
Key features of GSTR-3B- Summary Format: Unlike other GST returns such as GSTR-1, which require detailed invoice-level reporting, GSTR-3B provides a consolidated summary that eases compliance.
- Monthly Filing: It must be filed every month by all regular GST-registered taxpayers. The due date is typically the 20th of the month following the tax period.
- Mandatory Even When Nil: Filing is mandatory even if there are no transactions (nil returns).
- Tax Payment: Taxpayers pay the tax due along with filing the return.
- Non-revisable: Once filed, the return cannot be revised or corrected; errors must be adjusted in subsequent returns.
- Input Tax Credit Claim: It allows declaration of ITC availed during the period, subject to certain conditions and limits.
- GSTR-2A & GSTR-2B: These two are auto-generated input tax credit reports that buyers can use to verify the GST paid on their inward supplies. GSTR-2A is dynamic and changes as suppliers file their returns. GSTR-2B is a static monthly statement available to help reconcile input tax credit claims.
- GSTR-4: This is an annual return filled by taxpayers who have opted for the composition scheme. Unlike regular taxpayers who file monthly or quarterly returns, composition dealers file this return once a year, by the 30th of April following the financial year. It summarizes outward and inward supplies, tax paid, and liabilities for composition taxpayers with a turnover limit (typically up to Rs 1.5 crore). The quarterly filing requirement for composition was replaced by this annual return, streamlining compliance for small businesses opting for composition.
- GSTR-5: Filed by non-resident taxable persons who take taxable supplies in India but are not permanently established here. This return is filed monthly and contains details of all inward and outward supplies made by the non-resident.
- GSTR-6: Filed by Input Service Distributors (ISD) to distribute input tax credit to their branches or units. It details the ITC received and distributed among recipients.
- GSTR-7: Filed by tax deductors at source (TDS) under GST to report the tax deducted on payments made to suppliers. This return helps reconcile TDS records with the supplier’s return.
- GSTR-8: Filed by e-commerce operators who are required to collect tax at source (TCS) on supplies made through their platforms. This return reports the TCS collected from sellers on the marketplace.
- GSTR-9 & GSTR-9C: GSTR-9 is the annual return filed by regular taxpayers, consolidating the details of all monthly/quarterly returns filed during the financial year. GSTR-9C is a reconciliation statement and audit report mandated for taxpayers with turnover exceeding Rs 2 crore, that reconciles the annual returns with audited financial statements.
- GSTR 10: A taxable person whose GST registration is cancelled or surrendered has to file a return in Form GSTR-10 called the 'Final Return'. This is a statement of stocks held by such a taxpayer on the day immediately preceding the date from which cancellation is made effective.
- GSTR 11: Form GSTR-11 is a form to be filed by every registered person who has been issued a Unique Identity Number (UIN) to acquire tax credit/refunds under GST.
Know More About: Company Registration Services in Delhi India
GST Return Due Dates:
| GST Return Due Dates: | GST Return Due Dates: |
|---|---|
| GSTR 1 | The 11th day of the following month for taxpayers who file on a monthly basis, and the 13th day of the month following the end of each quarter for taxpayers who file on a quarterly basis. |
| GSTR-3B | Must be filed by the 20th of the following month, or by the 22nd or 24th in case of quarterly filers. |
| GSTR-2A & GSTR-2B | GSTR 2A from the 11th to the 15th of the month that follows the month in which the GST return is filed. GSTR-2B is the 14th of the following month, which is before filing ITC claims. |
| GSTR-4 | 30th of April following the relevant financial year. |
| GSTR-5 | By the 13th of the month following the tax period. |
| GSTR-6 | 13th of month following the relevant tax period. |
| GSTR-7 | 10th of the following month. |
| GSTR-8 | 10th of the following month. |
| GSTR-9 & GSTR-9C | GSTR-9 31st of December of next year for a particular financial year. GSTR-9C is December 31 of the respective financial year. |
| GSTR 10 | Within 3 months from the date of cancellation or date of cancellation order whichever is later. |
| GSTR 11 | 28th of the month following the month in which inward supply is received by the UIN holders. |
Register for GSTIN (if not already registered): To file GST returns, you must be a registered taxpayer with a valid GST Identification Number (GSTIN). GSTIN is a 15-digit unique code issued based on your PAN and state of operation.
Log in to the GST Portal (GST filing online): Visit the official GST portal: https://services.gst.gov.in/. Log in using your GSTIN and password.
- Access the Returns Dashboard: After logging in, navigate to Services > Returns > Returns Dashboard. Select the financial year and period for which you want to file; this choice is the starting point of the GST return process.
- Select the Return Form: Forms such as GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, or others appropriate for your business will be displayed. Choose the relevant form for GST return filing (e.g., GSTR-1 for outward supplies, GSTR-3B for summary return). Select Prepare Online to start filling the form.
- Enter Return Details: Fill in your sales, purchases, tax paid, input tax credit details, and other relevant data as per the form. Ensure all information is accurate to avoid mismatches or errors. Save the form after entering details.
- Submit the Return: Review the entered details and click Submit. Check the return status to confirm it has changed to Submitted.
- Make Payment of Tax (if applicable): Go to the Payment of Tax section. Click on Check Balance to view your available input tax credit and cash balances. Use Offset Liability to pay any remaining tax liability using cash or credit.
- File the Return with Verification: Complete the final stage of the GST return process by electing the authorized signatory. Use either your Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or Electronic Verification Code (EVC) to verify and file the return. Before beginning the GST return filing process, ensure you are aware of the applicable GST return due dates to avoid late fees and interest.
- Acknowledgement and Confirmation: After successful filing, an acknowledgement or ARN (Application Reference Number) is generated. Keep this for your records and future reference.
- Entering details like GSTIN, invoice numbers, tax amounts, or supplier details manually can lead to mistakes. Even small errors can cause mismatches or be considered fraudulent. Double-check all entries or use reliable GST filing software with validation features to minimize errors.
- Reporting different sales/turnover values in GSTR-1 (invoice-level details) and GSTR-3B (summary return) is a frequent mistake. Always reconcile your invoices and returns regularly to ensure consistency.
- Even if there are no sales or purchases in a tax period, filing NIL returns is mandatory. Skipping NIL returns can lead to penalties.
- Zero-rated supplies (like exports) and nil-rated supplies (those attracting 0% GST) are reported differently. Mistakes here could cause issues in claiming input tax credit or compliance.
- Many taxpayers fail to declare liability under reverse charge or miss claiming associated input tax credit properly.
- Claiming ITC on blocked goods/services or on ineligible invoices can lead to disallowance and penalties under Section 17(5).
- Not verifying returns properly or ignoring notices and alerts on the GST portal can escalate compliance issues.
- Missing GST return due dates is one of the most common compliance mistakes, leading to penalties, late fees, and blocked ITC.
- Lack of proper invoice and GST record maintenance complicates filing accurate returns and responding to audits.
- Errors in data entry or mismatches during reconciliation can disrupt the GST return process and lead to notices or penalties.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of GST returns, such as GSTR-1 for outward supplies, GSTR-3B for summary tax payment, and other specialized returns like GSTR-4, GSTR-5, GSTR-6, GSTR-7, GSTR-8, and annual returns GSTR-9/9C - is essential for maintaining compliance under India’s GST regime.
Each form serves a specific purpose, caters to a different category of taxpayer, and comes with its own filing frequency and due dates. Timely and accurate filing not only helps businesses avoid late fees, penalties, and interest but also ensures smooth input tax credit claims and builds a transparent tax profile. By understanding the applicability of each form and following best practices, taxpayers can make GST return filing smoother and focus on business growth.
We offer quick and hassle-free GST registration and compliance services across India. From GST return filing to expert guidance on due dates, our team ensures smooth tax compliance for your business. Get started today and simplify your GST journey with our trusted professionals.
Read Also:Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) –
Q.1 What is a GST return?A GST return is a document filed by registered taxpayers to report details of their sales, purchases, output tax collected, and input tax paid during a specific tax period. It ensures compliance with India’s Goods and Services Tax regulations.
Q.2 Who is required to file GST returns?All entities registered under GST - including regular taxpayers, composition dealers, non-resident taxable persons, e-commerce operators, TDS deductors, and Input Service Distributors - must file GST returns as per their applicable due dates.
Q.3 Can I file GST returns online?Yes. GST returns can be filed online via the official GST portal (https://services.gst.gov.in/) by logging in with your GSTIN and credentials, selecting the relevant return form, entering the details, and submitting it with verification.
Q.4 Is it necessary to file NIL returns?Yes. Even if there are no sales or purchases in a tax period, registered taxpayers must file NIL returns to remain compliant.
Q.5 What are the different types of GST returns?The different types of GST returns include GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, GSTR-2A, GSTR-2B, GSTR-4, GSTR-5, GSTR-6, GSTR-7, GSTR-8, GSTR-9, GSTR-9C, GSTR-10, and GSTR-11.

